Rigs report: EPC spending will rise 250% over 2020, says analyst
Speaking to delegates at the Annual Offshore Support Journal Virtual Conference & Exhibition, Westwood Global Energy head of offshore Thom Payne said, “Now on the surface, this outlook may appear optimistic, particularly to an industry still reeling from the latest downturn in a downturn, but it must be regarded in the context of late 2019 when sentiment was arguably at a five-year high.”
Putting it in context, Mr Payne called 2020 “one of the most challenging years in the history of the global oil market,” noting the weak levels of EPC spending – “one of the worst years on record.”
Reacting quickly to the Covid-19 energy demand destruction and plummeting price of oil caused by the Saudi-Russia price war, oil and gas companies slashed capex by an estimated 30%, he said, deferring or stalling around US$41Bn of planned 2020 offshore EPC contract value. “Of the US$12.3Bn of EPC awards actually recorded in 2020, 75% of this was accounted for by just five E&Ps across 23 projects, the five largest of which contributed around 57% of total spend and included Woodside Sangomar, ExxonMobil’s Payara and Petrobras’ Mero 3,” said Mr Payne.
Basing its outlook on a US$57 per barrel price, Westwood Global Energy expects total offshore EPC investment at US$44.4Bn in 2021 – a year-on-year increase of some 250%. Brent crude oil futures were trading at US$64.62 per barrel for May contracts on 22 March.
Mr Payne noted that a significant portion of the EPC spending in 2021 was made up of ‘half-pregnant’ projects with substantial pre-FID commitments delayed in 2020.
Among these are Shell’s Whale, Equinor’s Bacalhau and Qatar Petroleum’s North Field projects which have commenced partial construction of long-lead EPC items such as FPSOs or platform infrastructure, accounting for an estimated US$7.7Bn in 2021. Other areas of big spending will be deferred rewards that are critical to backfilling LNG trains or supporting existing gas sales agreements in Australia, with a combined EPC value of about US$4.8Bn, according to Mr Payne.
Petrobras will be a key driver of business, making US$6.5Bn in EPC awards in Brazil pre-salt basin drilling activity.
In his presentation, Mr Payne said offshore drilling felt the brunt of Covid-19, noting that contracting of drill ships, semi-submersibles and jack-ups began to deteriorate in March 2020, “with counts falling by 85 units and over US$2.4Bn worth of backlog being wiped out.”
Mr Payne expects offshore drilling levels to stabilise in 2021, increasing by 40 units over the course of the year, but still below pre-pandemic levels. The bright spots will be the Middle East, Latin America and the North Sea.
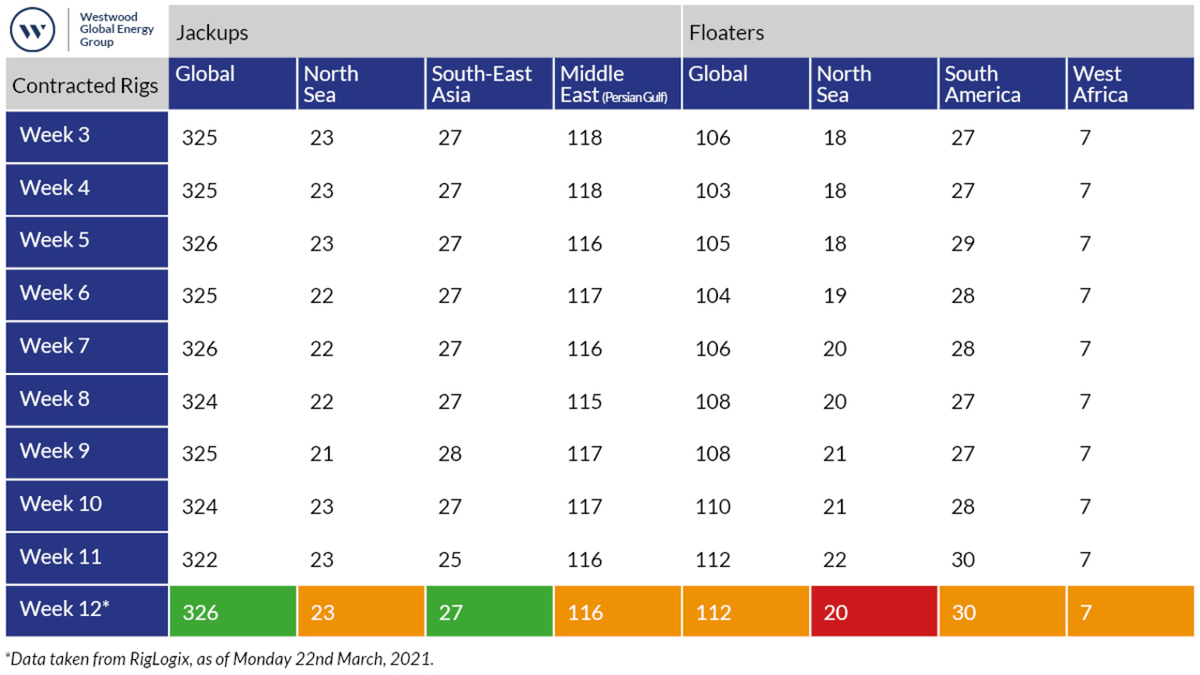
Current drilling activity
Led by an uptick in southeast Asia, global offshore jack-up rig activity rose week-on-week by four units — its biggest jump of 2021 – during week 11 of the year.
Westwood Global Energy Group’s RigLogix reported 326 offshore jack-up rigs were contracted during week 12 2021, with 27 units drilling in southeast Asia, up week-on-week from 25. Jack-up rig activity in the North Sea and the Middle East remain stable.
Meanwhile, deepwater drilling activity remained unchanged week-on-week, with 112 floaters – semi-submersibles, drill ships and other mobile offshore drilling units (MODUS) – contracted worldwide. This is despite a slippage of two units in the North Sea week-on-week, with active units falling to 20.
by John Snyder
Source: Riviera, 2021/3/24